Emulating the Badge Under Renode
(Eventually)
Sean "xobs" Cross
About Me
Talk Outline
- What is Renode?
- How is it extensible?
- What is the state of the badge?
What is Renode?
Renode is an Emulator
- Windows
- Mac
- Linux
- CI
- Github Actions
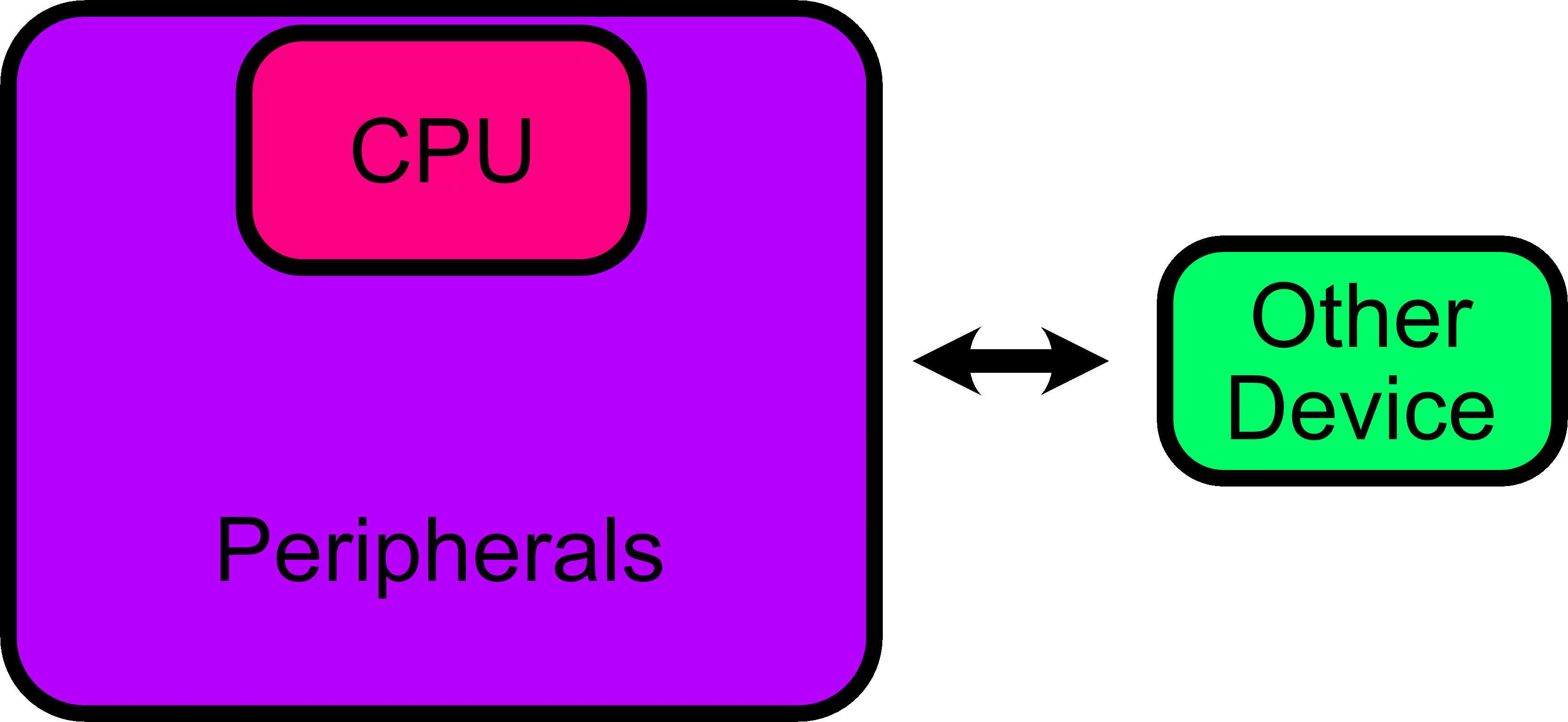
Whole-system Emulator
- CPU cores
- Peripherals
- Interconnections
Whole-system Emulator
CPU Cores
- x86
- arm
- arm64
- ppc
- riscv
- spark
- xtensa
Peripherals
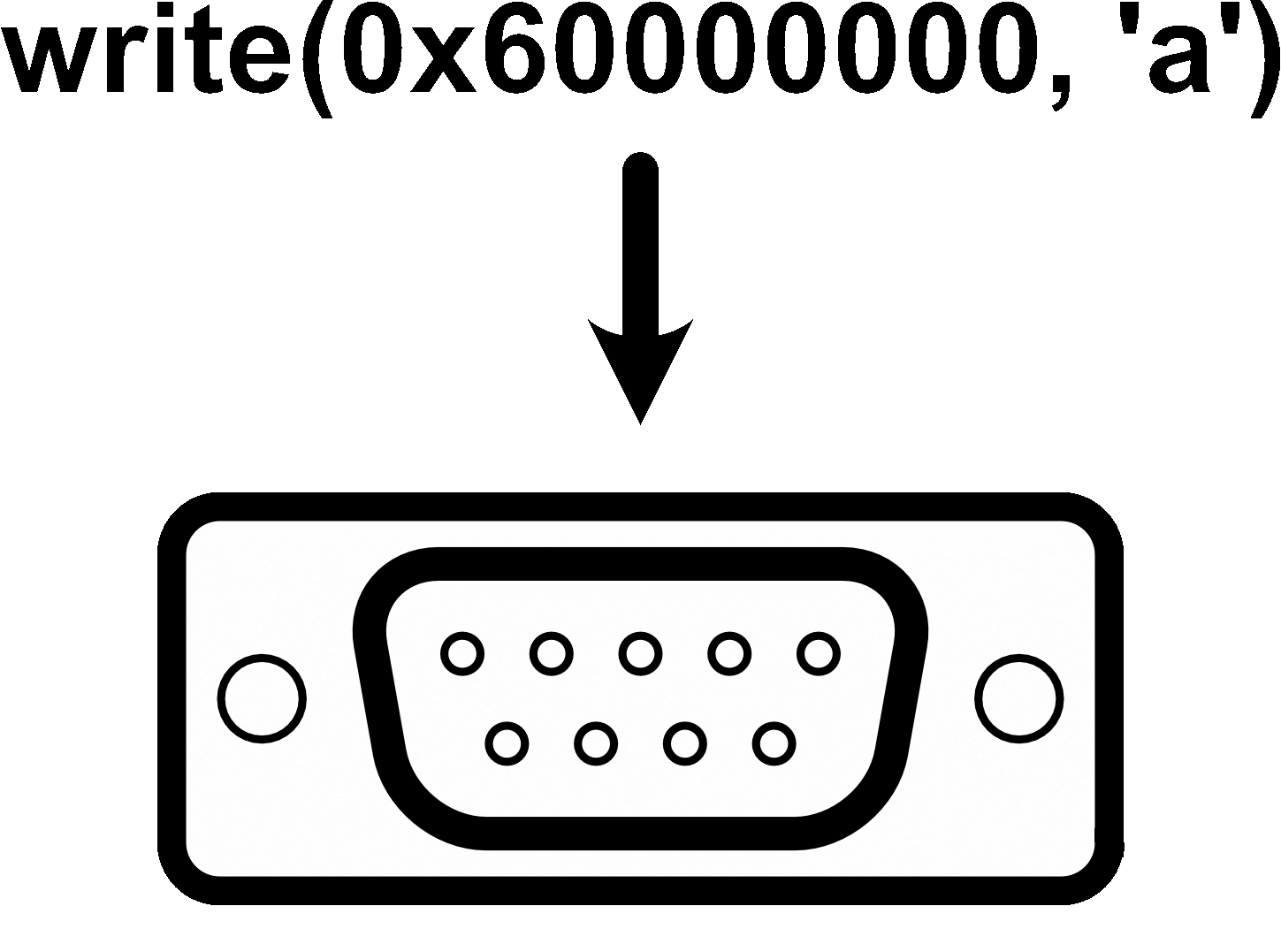
Peripherals Are Just Special Memory
- Writing to a memory address does a thing
- Reading from an address gets a result
- Interrupts are just GPIOs
Peripherals Are Just Special Memory
10% of the Functionality Gets You 90% of the Way There
- E.g. in a serial device, baudrate, timers, and parity/stop can be ignored
- Just "Tx", "Rx", and interrupt setup
- Most software works just fine if you return zeroes for invalid addresses
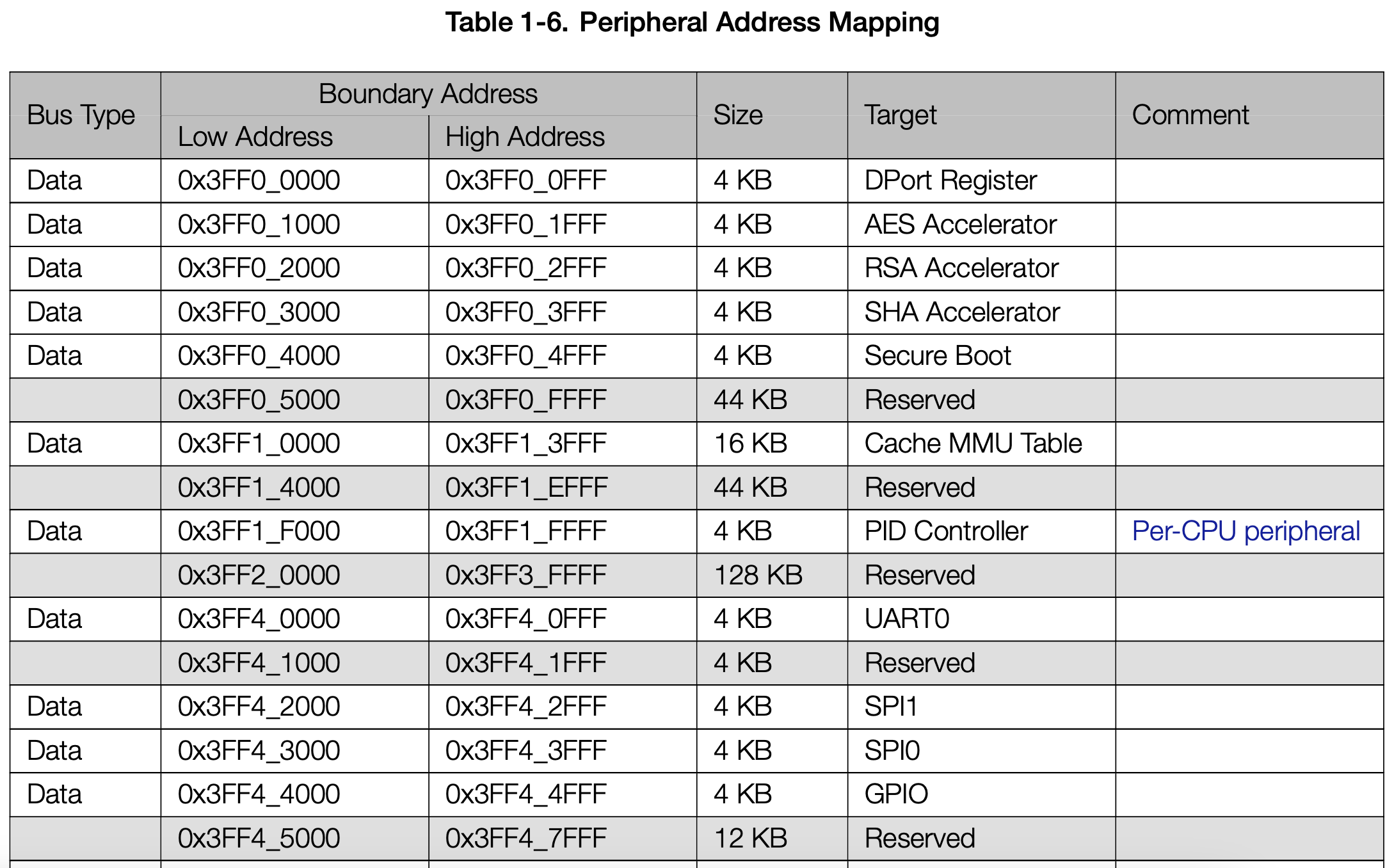
SVD files are your friend
- Your chip probably comes with a SVD file
- This gives a map of RAM and peripherals
- Renode can parse this and use it for logging / defaults
Existing Peripherals in Renode
- Built-in peripherals for a number of devices
- STM32
- NRF52
- IMXRT
- LiteX
- See https://github.com/renode/renode-infrastructure/tree/master/src/Emulator/Peripherals/Peripherals for more
Creating Peripherals
- Renode is written in C#
- Like Java, C# has an
eval()function - Peripherals can be written and loaded at runtime
Networks in Renode
- Built-in support for CAN, Ethernet, and Wireless
- Also possible to add networks at runtime
- No latency, just packets of data
- Different devices run at different speeds
Other Goodies
- LCD monitor with touchscreen support
- Python interpreter for quick hacks
- Attach GDB to any CPU core
- Attach a serial port to a network connection
- Scriptable with Robot framework
- Log function calls
Shortcomings
- Unable to unload modules
- Need to restart Renode when you change a file
- No real audio support
- Support for verifying I2S, but can't play it
- Only x64 hosts
- Runs under Rosetta on Mac
- Documentation needs work
- Use the source!
Extending Renode
First, Betrusted
- FPGA with VexRiscv
- 2nd FPGA with smaller VexRiscv
- 16-bit COM bus between them
- AES extensions
- x25519 "ENGINE" accelerator
- SHA accelerator
- Battery charger and manager
- Custom lcd, timers, and USB
Emulating it under Renode
- Good enough to develop the OS!
- Good enough to catch bugs
ENGINE bug
- Added test vectors to the OS
- Ran test vectors on physical device
- Got test vectors passing in Renode
-
- Yay!
- Someone (without a device!) decided to add more vectors
- Tested in Renode
- Passed
- Failed on hardware
- Bug in detecting overflow condition for normalization in hardware
- https://github.com/betrusted-io/gateware/commit/817e284a3d92037b8cb0686735578d2bb60853e9
Getting Started with Renode
- Renode Platform Definition (
.repl) - Renode Script (
.resc)
Example project repl
Example project resc
Running it
How to Extend Renode
- Find a peripheral that does what you want
-
- You might even find a compatible peripheral!
- Copy it to your project
- Change the constructor
- Change the register set
- Import the `.cs` file into Renode
- Add it to your platform file
Demonstration!
Running Badge Software in Renode
It Doesn't
Xtensa is an Uncommon Architecture
- Audio DSPs
- Possibly Intel?
- NXP
Extensive use of Boot ROM
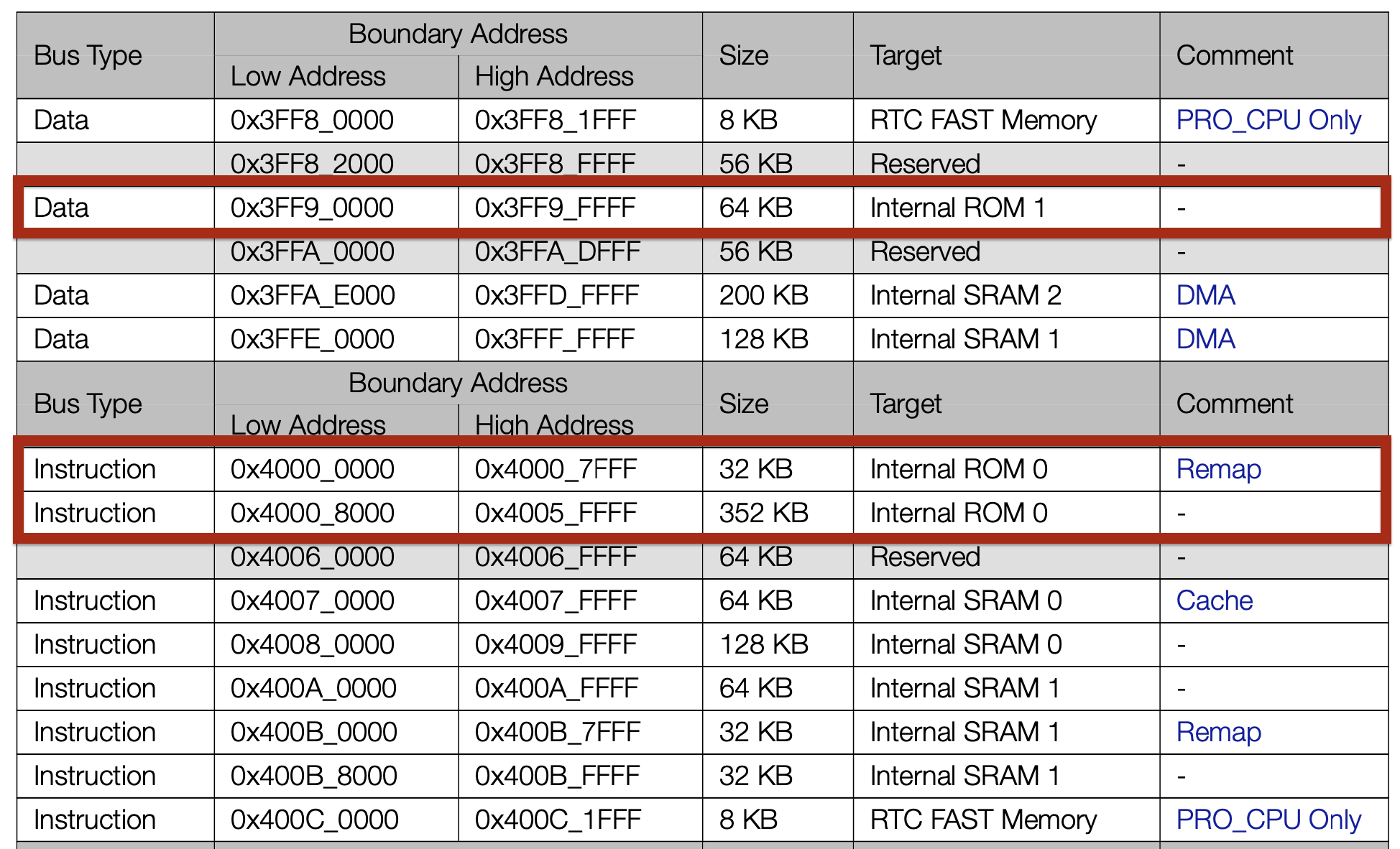
Extensive use of Boot ROM
$ esptool.py dump_mem \
0x3ff90000 \
65536 \
irom.binAdd a serial port
namespace Antmicro.Renode.Peripherals.UART {
public class ESP32_UART : UARTBase, IDoubleWordPeripheral,
IKnownSize {
private readonly DoubleWordRegisterCollection registers;
public ESP32_UART(Machine machine) : base(machine) {
registers = new DoubleWordRegisterCollection(this,
new Dictionary<long, DoubleWordRegister> {
{0x00, new DoubleWordRegister(this).WithValueField(0,8,
writeCallback: (_, v) => TransmitCharacter((byte)v))}
});
}Add a serial port
{0x00, new DoubleWordRegister(this)
.WithValueField(0, 8,
writeCallback: (_, v) => TransmitCharacter((byte)v))}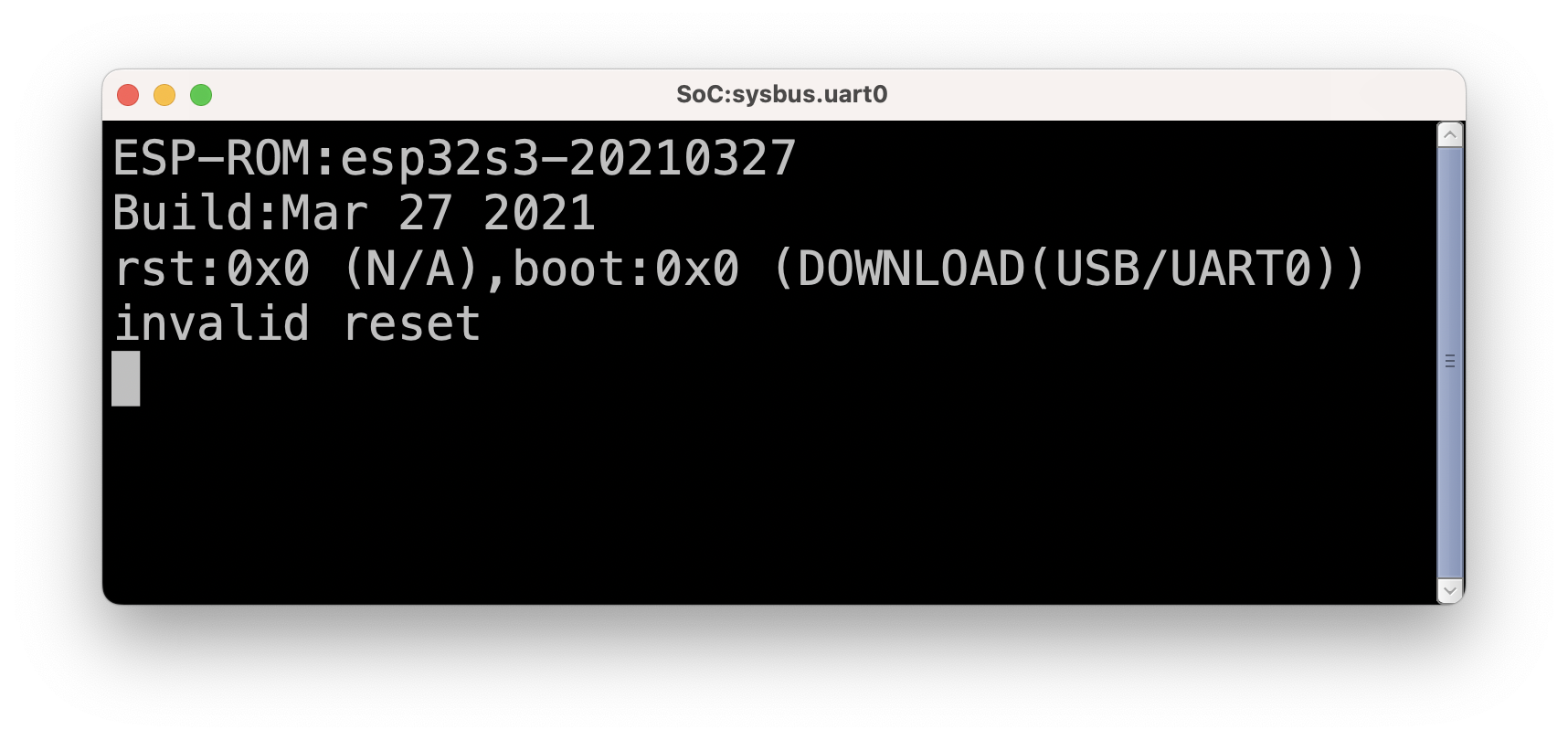
Load SVD file
sysbus:
init:
ApplySVD @esp32s3.svdLoad SVD file
extmem: Unhandled read from offset 0x64.
extmem: Unhandled write to offset 0x64, value 0x3.
sysbus: Read from an unimplemented register SYSTEM:SYSCLK_CONF
(0x600C0060), returning a value from SVD: 0x1. (3)
sysbus: Read from an unimplemented register SYSTEM:PERIP_CLK_EN0
(0x600C0018), returning a value from SVD: 0xF9C1E06F.
sysbus: Write of value 0xF9C1E06F to an unimplemented register
SYSTEM:PERIP_CLK_EN0 (0x600C0018) generated from SVD.
sysbus: Read from an unimplemented register SYSTEM:PERIP_RST_EN0
(0x600C0020), returning a value from SVD: 0x0.
sysbus: Write of value 0x0 to an unimplemented register SYSTEM:PERIP_RST_EN0
0x600C0020) generated from SVD.
sysbus: Read from an unimplemented register SYSTEM:PERIP_RST_EN0
(0x600C0020), returning a value from SVD: 0x0.
sysbus: Write of value 0x4 to an unimplemented register SYSTEM:PERIP_RST_EN0 (0x600C0020) generated from SVD.
Add Peripherals
Slowly Advance
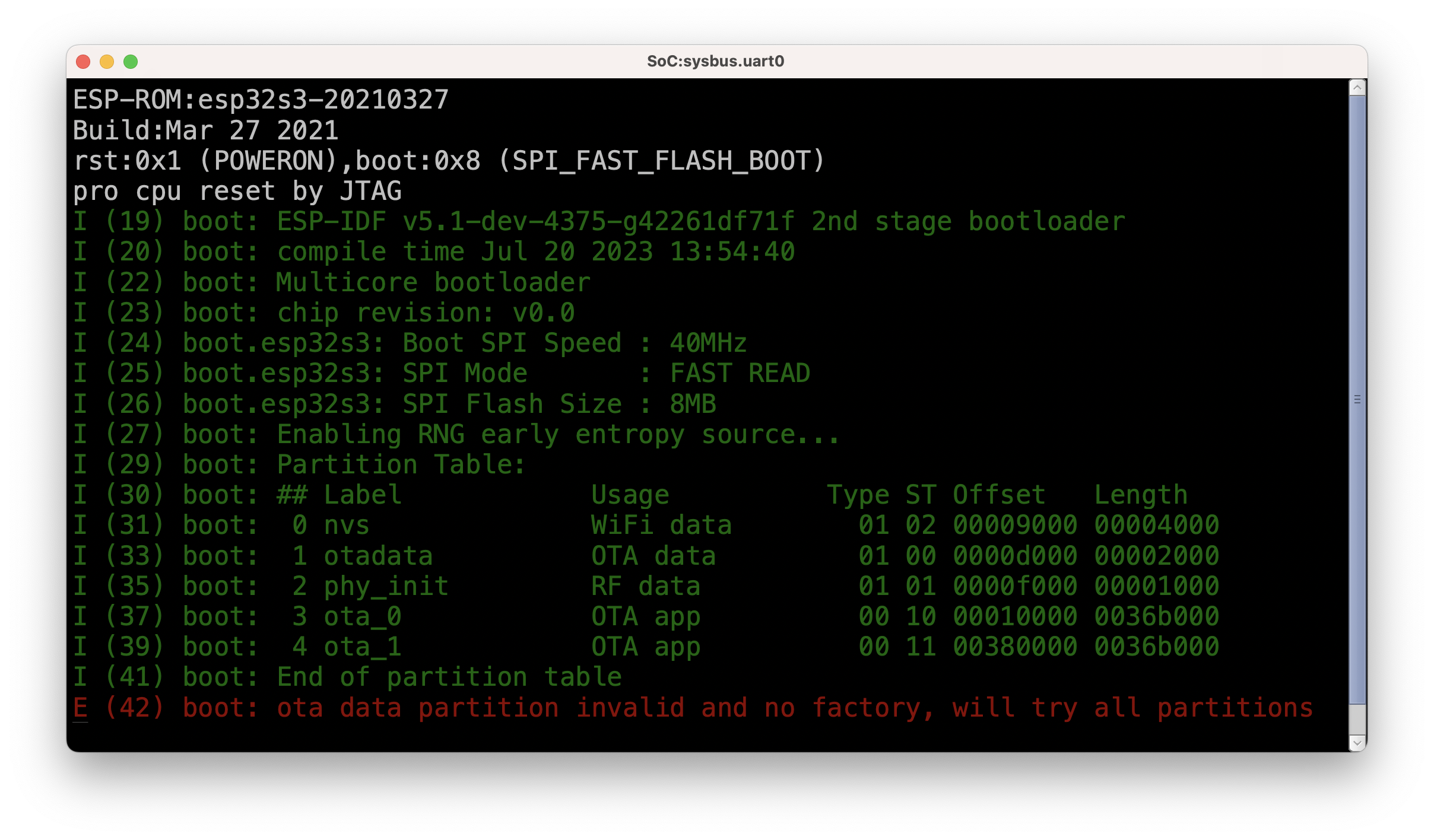
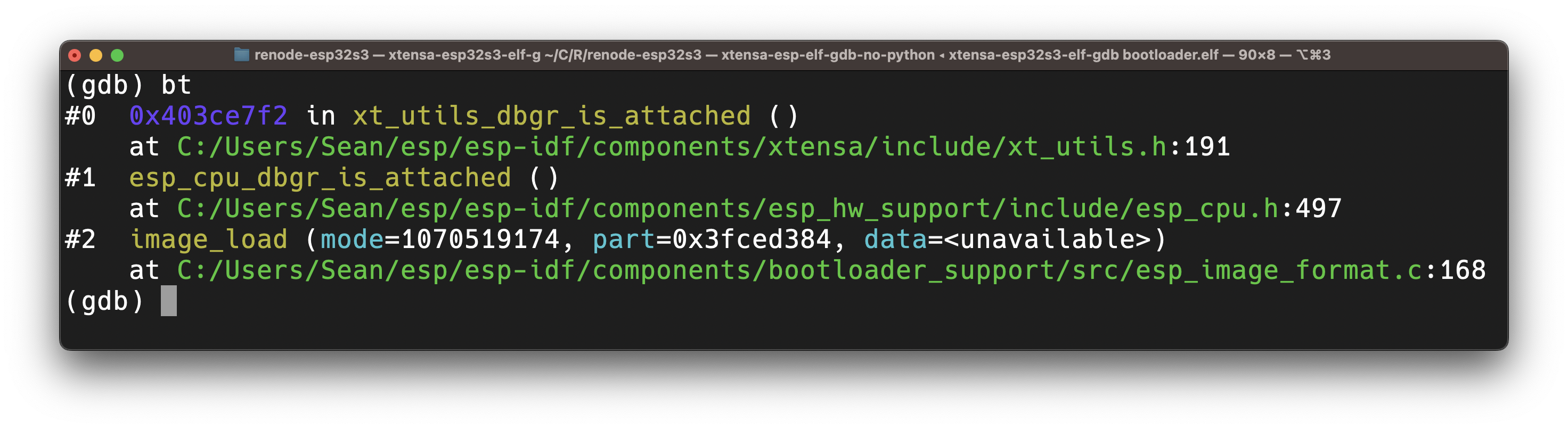
GDB with ELF
What's Left?
- SPI Controller
- Interrupt Controller
Getting involved
- Try Renode for your projects!
- Add CI tests for your firmware!
- Explore binaries for unknown targets!